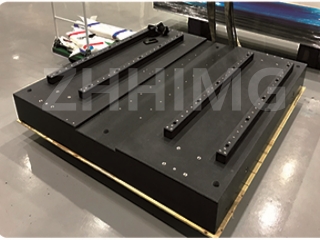
Granite is a natural igneous rock composed mainly of quartz, feldspar and mica, and has unique applications in the aerospace industry, especially in the field of optical devices. The use of granite in this field stems from its excellent properties, which are essential for the precision and reliability required in aerospace applications.
One of granite's main advantages is its inherent stability. Unlike many synthetic materials, granite has minimal thermal expansion, which is critical for optical components that must maintain precise alignment under varying temperature conditions. This stability ensures that optical systems such as telescopes and sensors operate accurately in the harsh environment of space.
Additionally, granite’s density and hardness make it a vibration-damping material. In aerospace applications, even the slightest vibrations can cause significant errors in optical measurements. By using granite as a stand or mounting material for optical equipment, engineers can dampen these vibrations, thereby improving the performance and life of the instrument.
Granite's natural polishing properties also play a vital role in optical applications. Granite's smooth surface can be finely processed to create high-quality optical components such as lenses and mirrors, which are essential for capturing and focusing light in various aerospace systems. This ability enables granite to produce components that meet the rigorous requirements of modern aerospace technology.
In summary, the use of granite in aerospace optics demonstrates the unique properties of this material. Its stability, shock absorption properties, and fine polishing capabilities make it an ideal choice for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of optical systems in the demanding aerospace environment. As technology continues to advance, granite will likely remain a key material in the development of cutting-edge aerospace optics.
Post time: Jan-13-2025